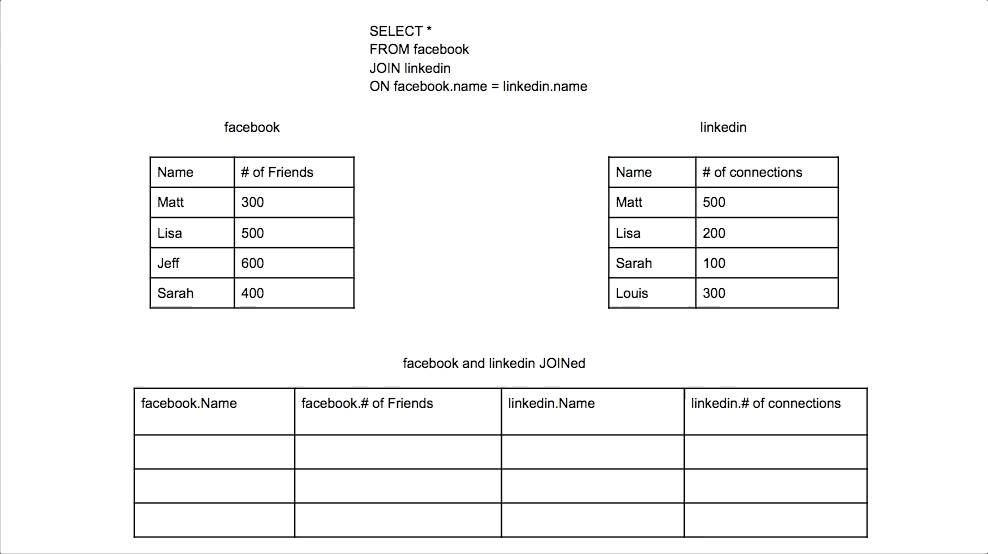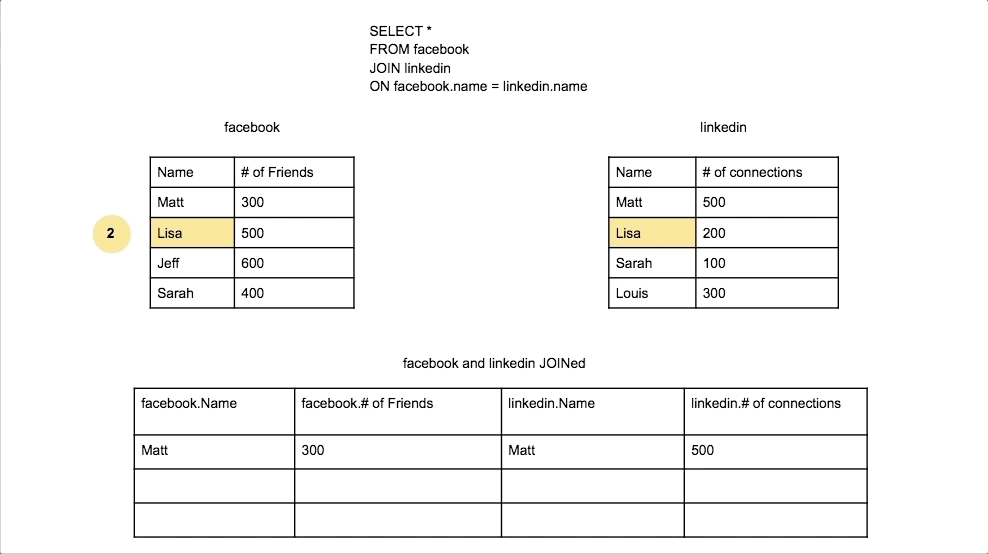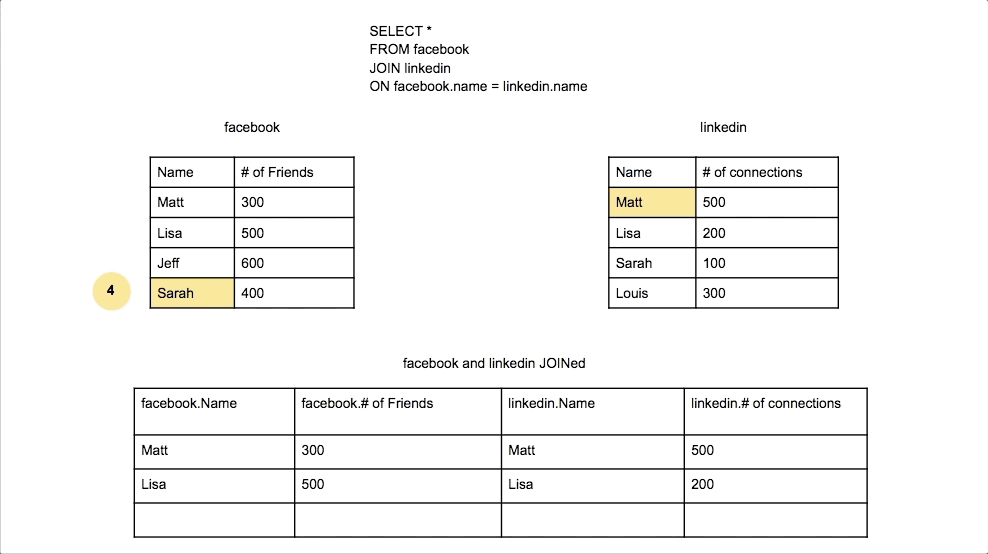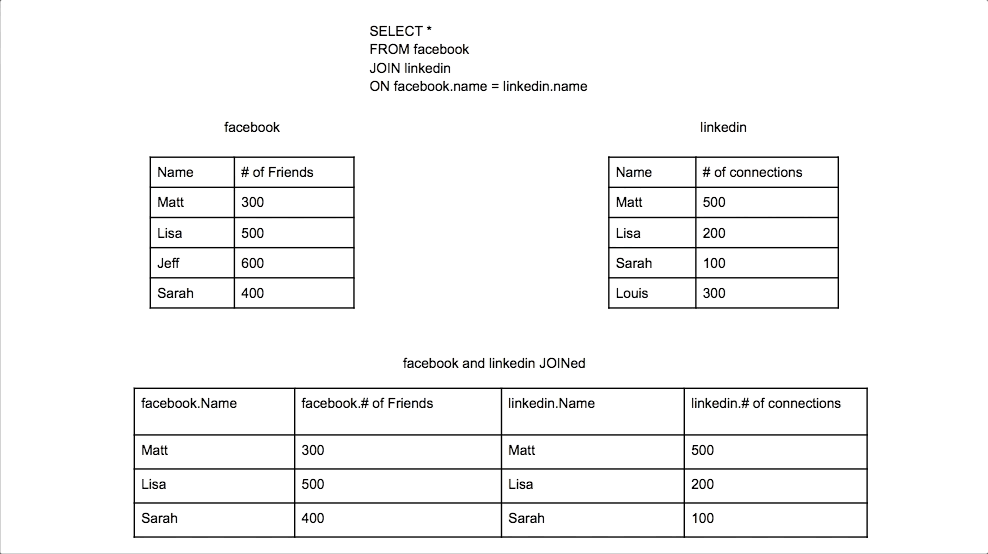
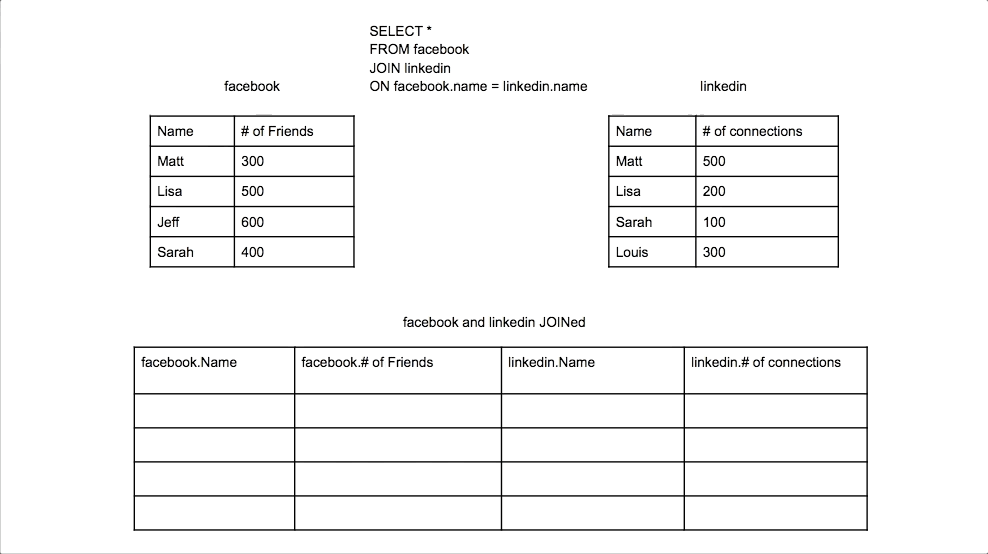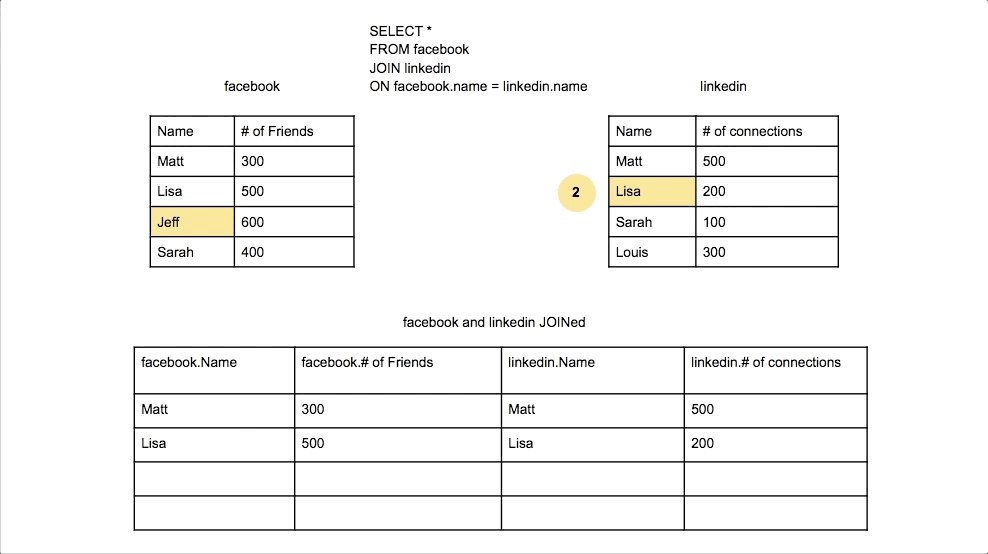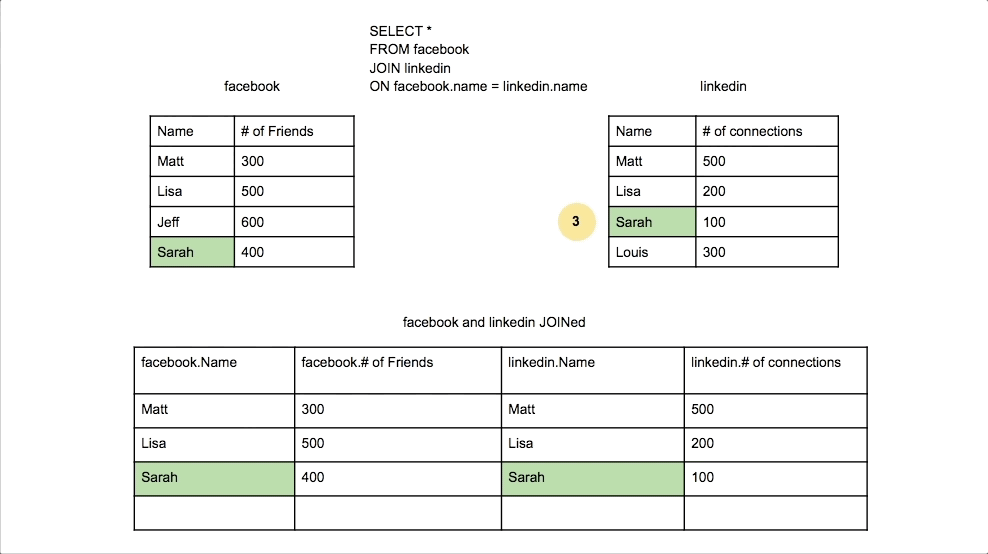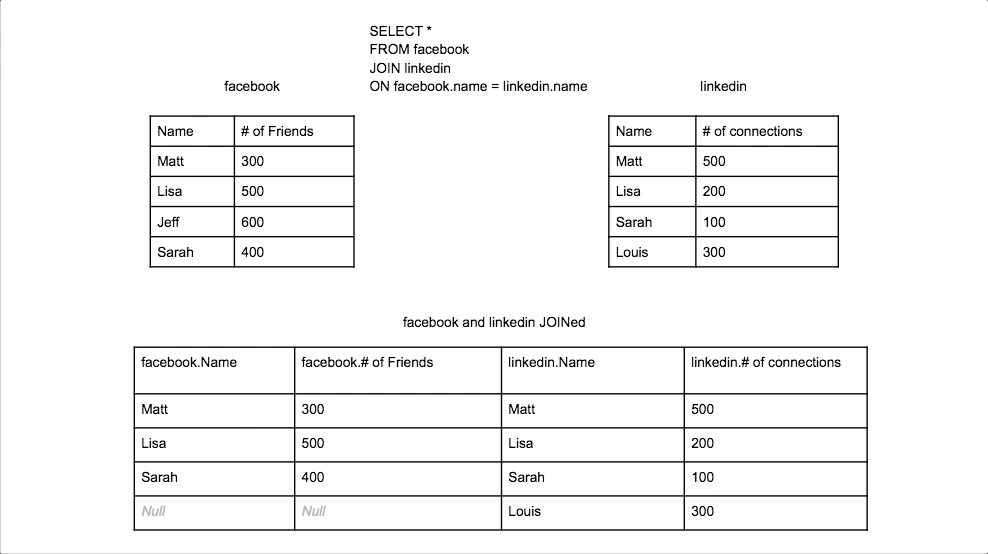
Inner Join
Combines rows from two tables where there is a match in both tables. Only matching rows are returned.
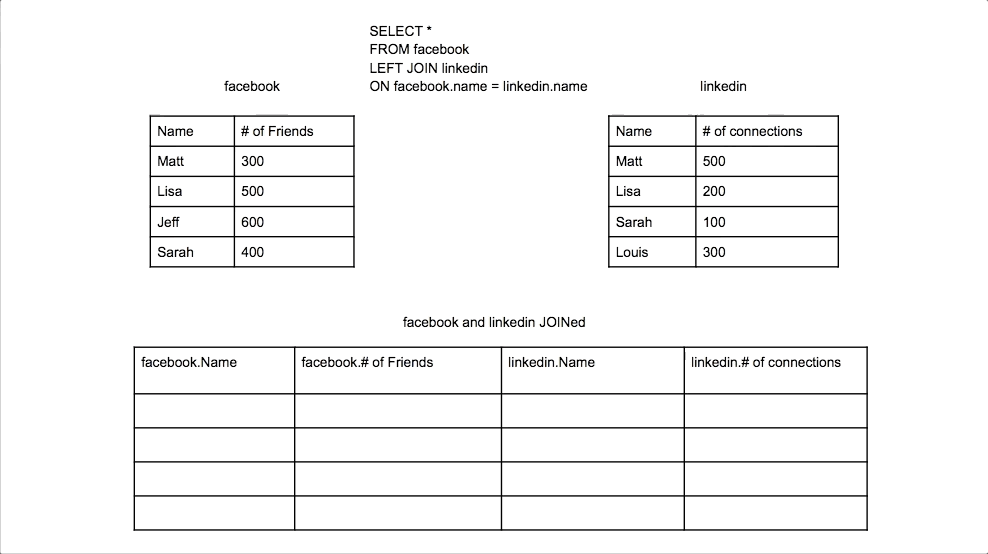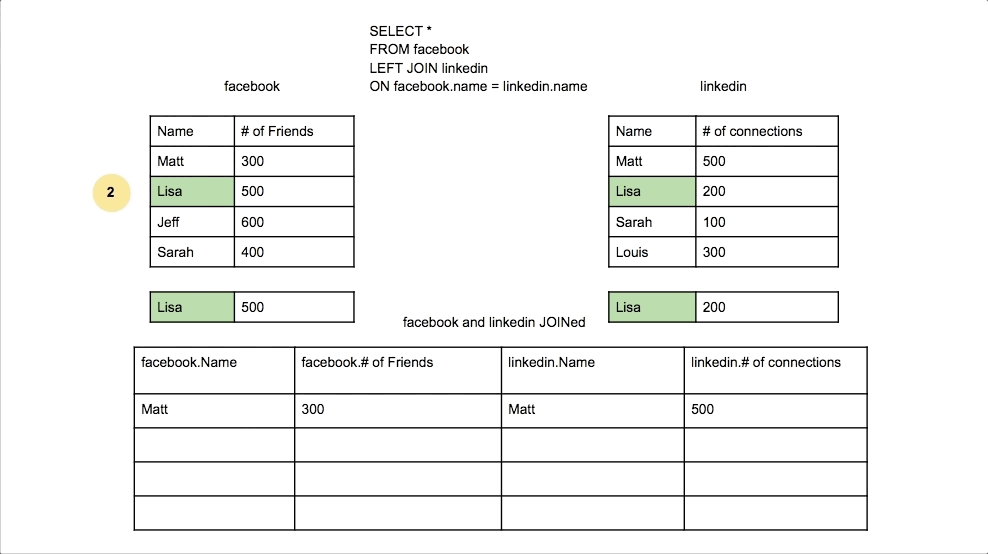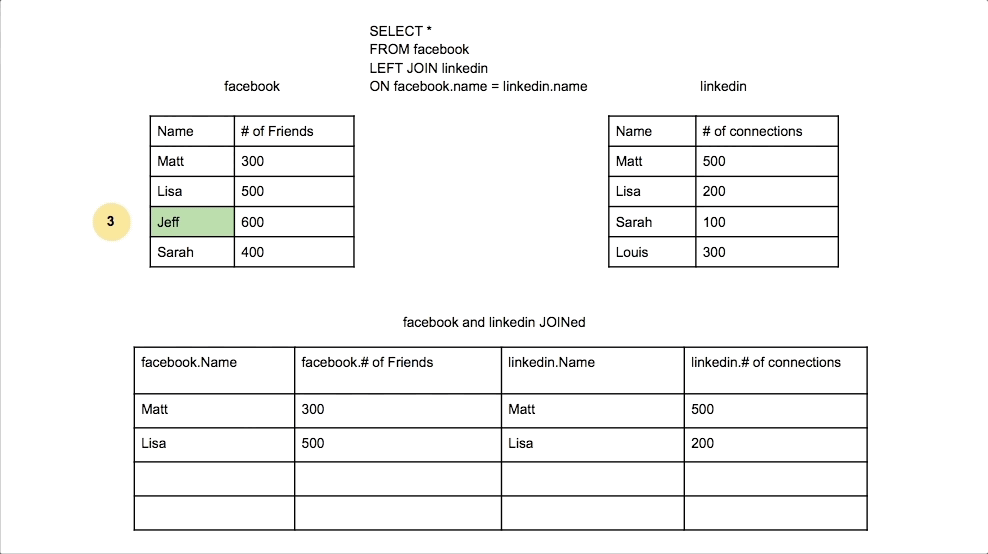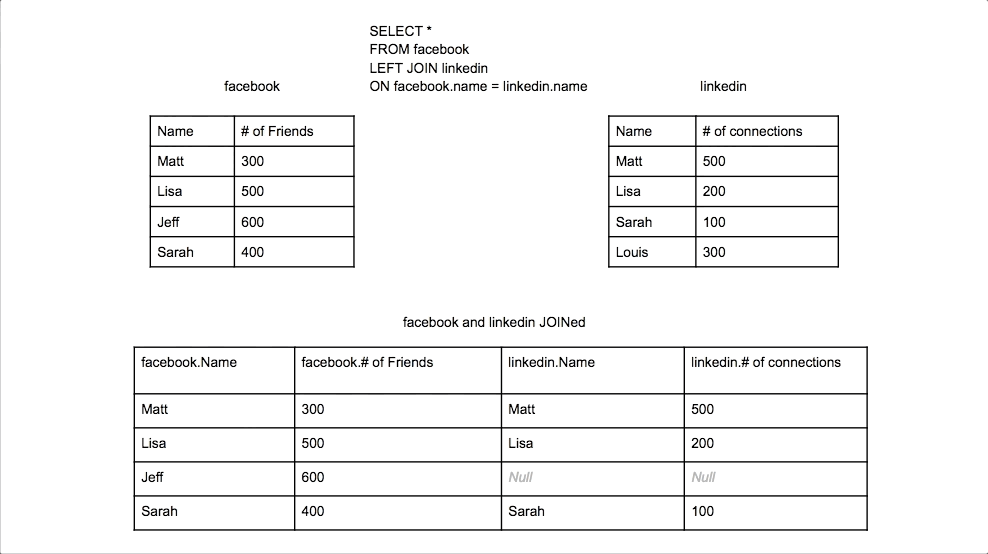
Left Join
Returns all rows from the left table, and the matched rows from the right table. Unmatched rows will show NULL.
Right Join
Returns all rows from the right table, and the matched rows from the left table. Unmatched rows will show NULL.
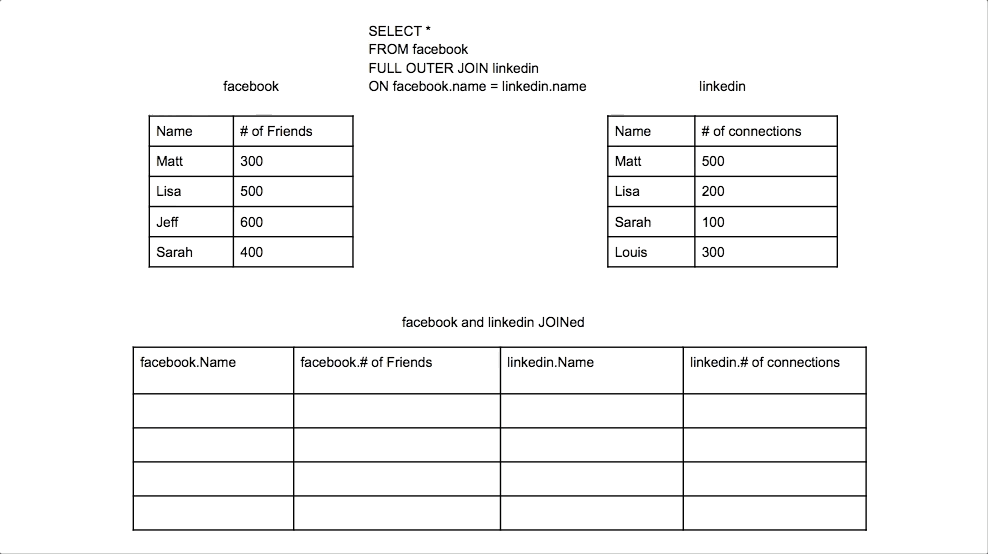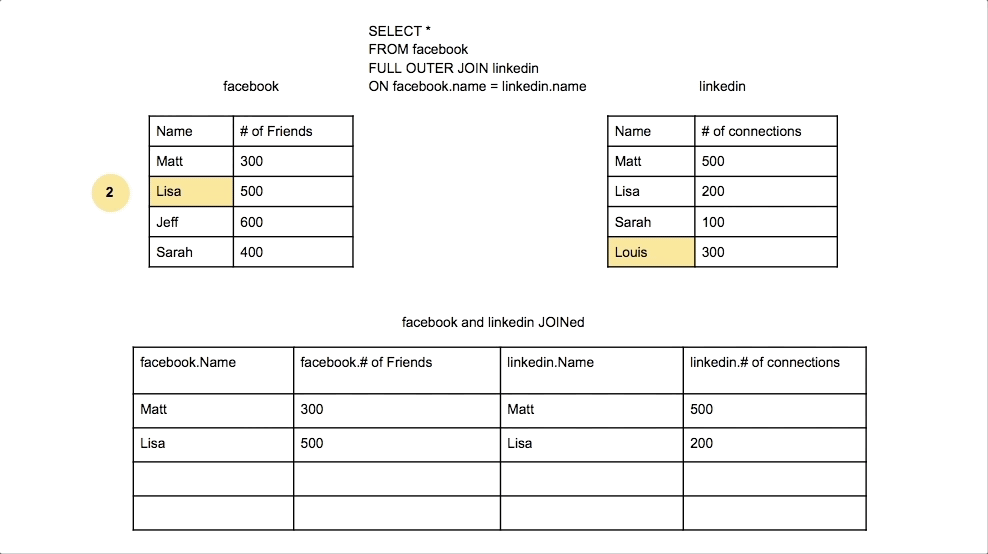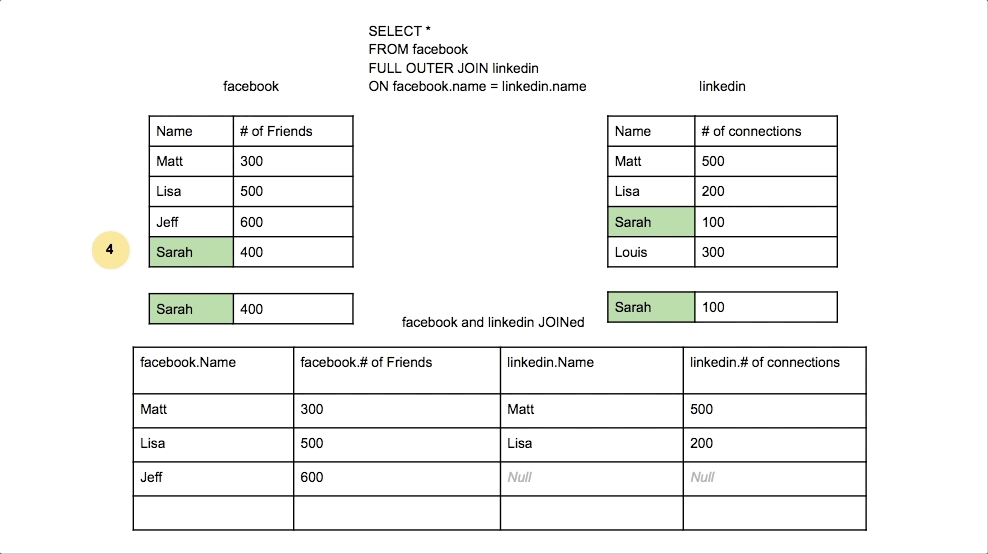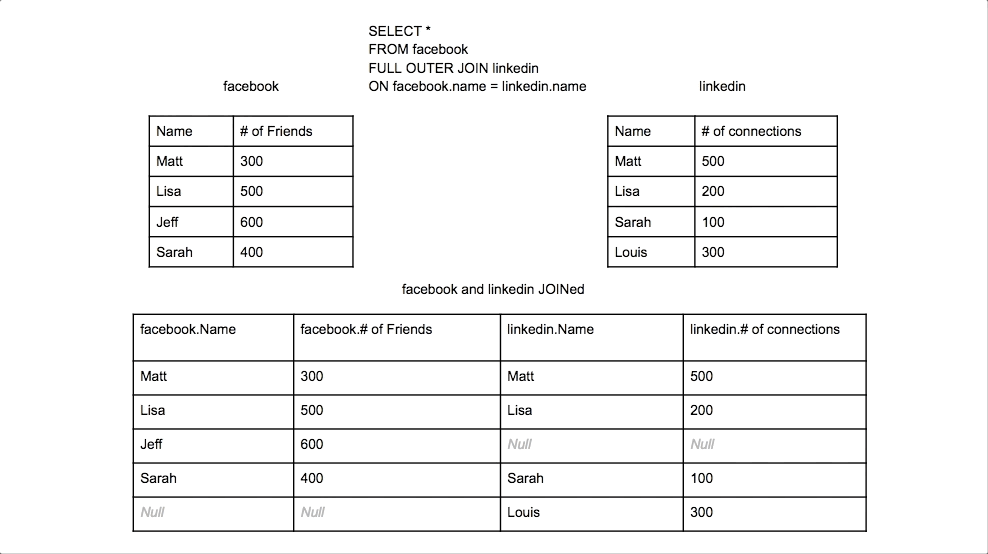
Full Outer Join
Returns all rows from both tables, with NULLs where there is no match.
Cross Join
A Cross Join produces a Cartesian product of the two tables. Every row from the first table is combined with every row from the second table.
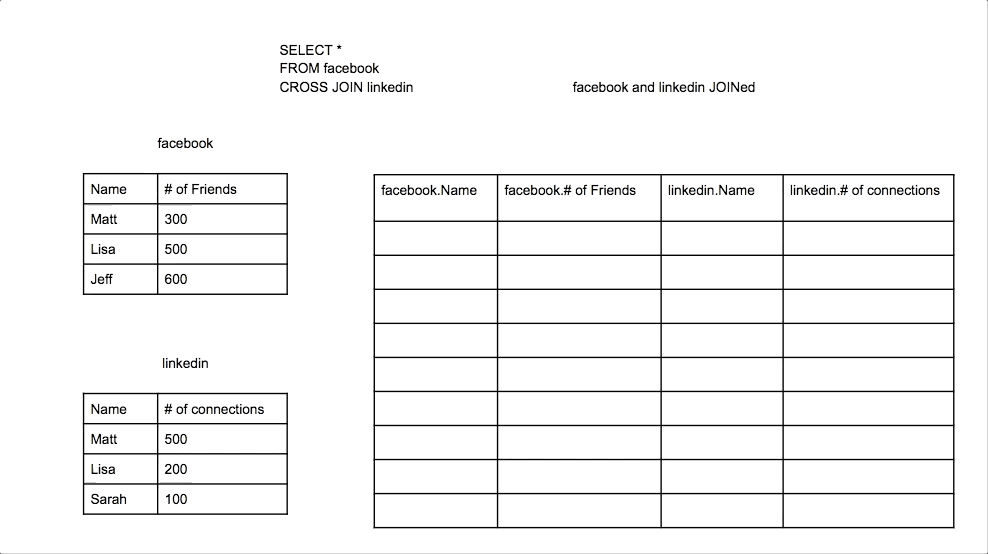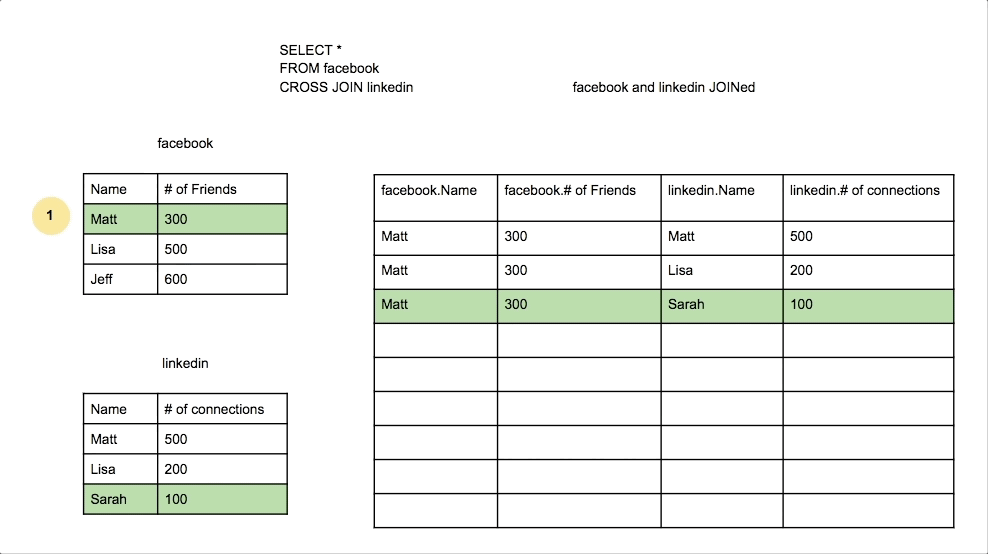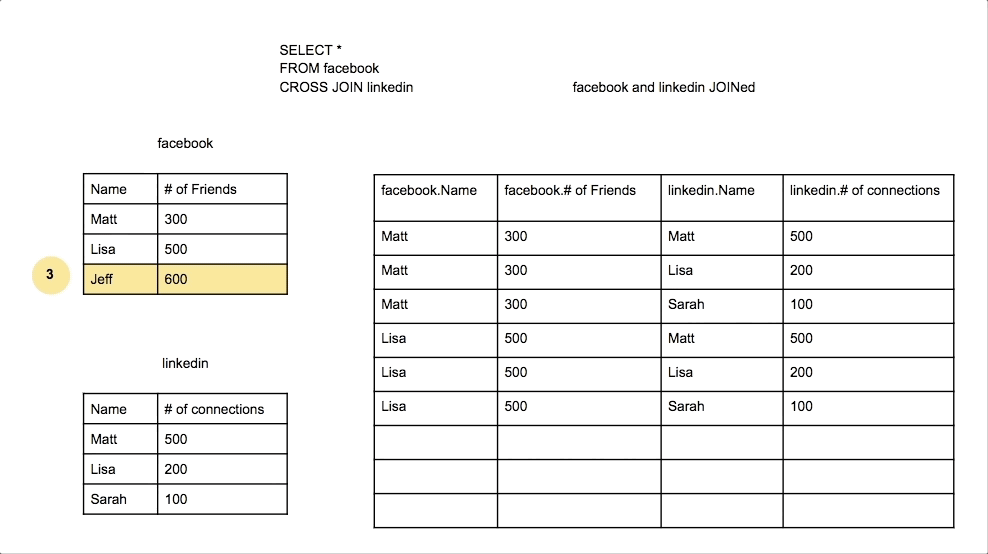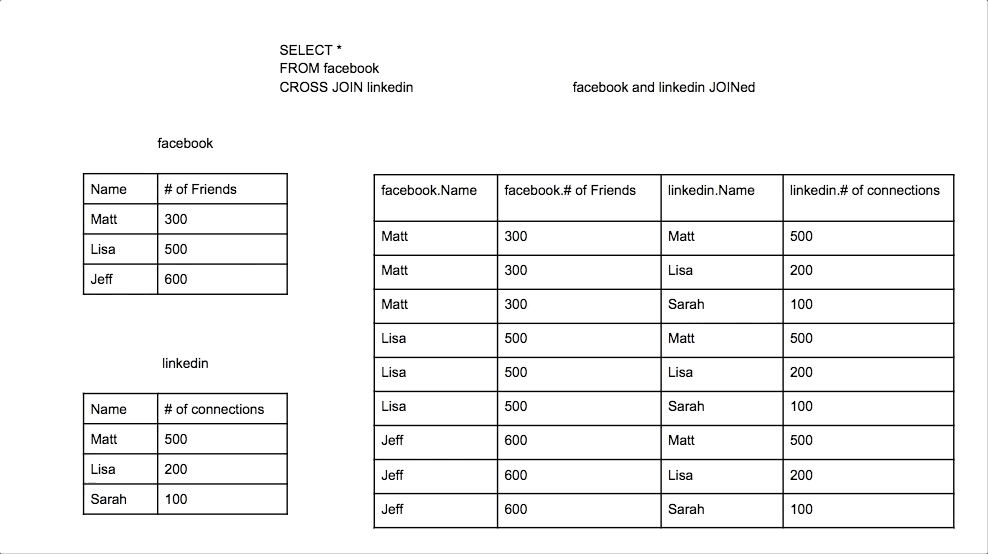
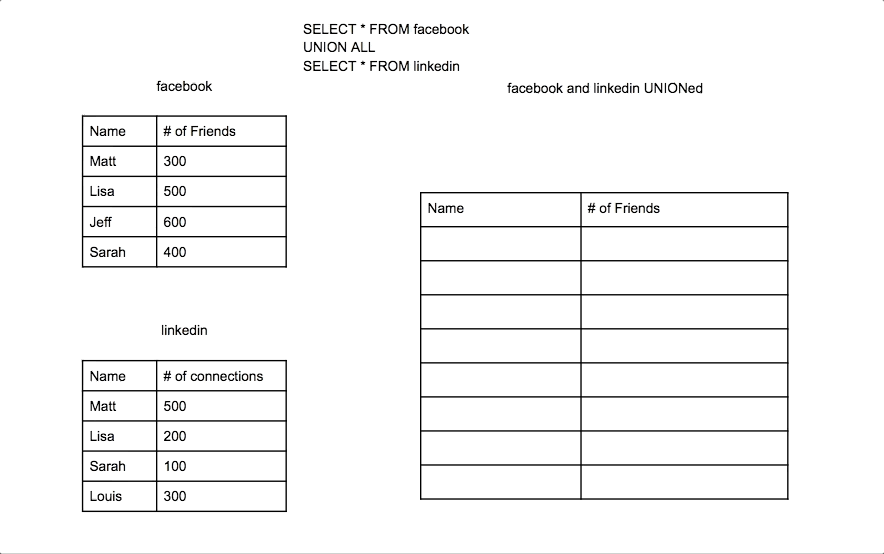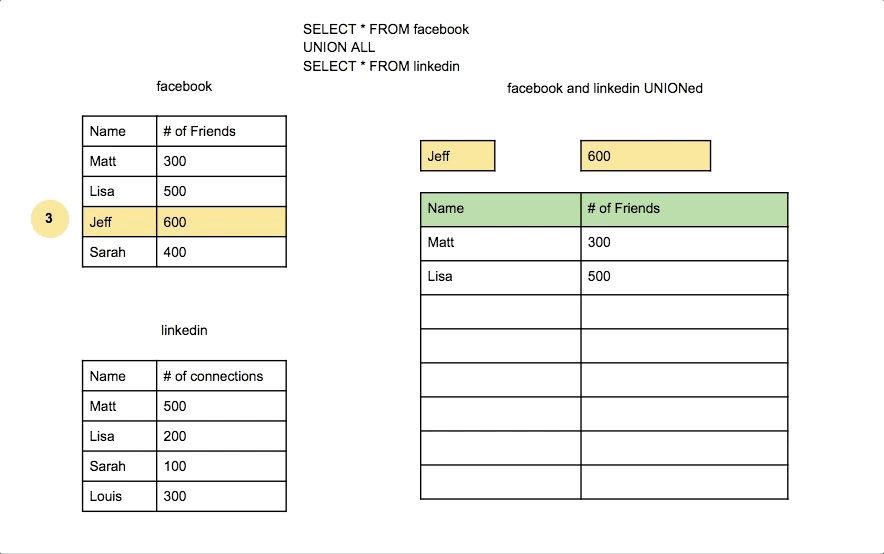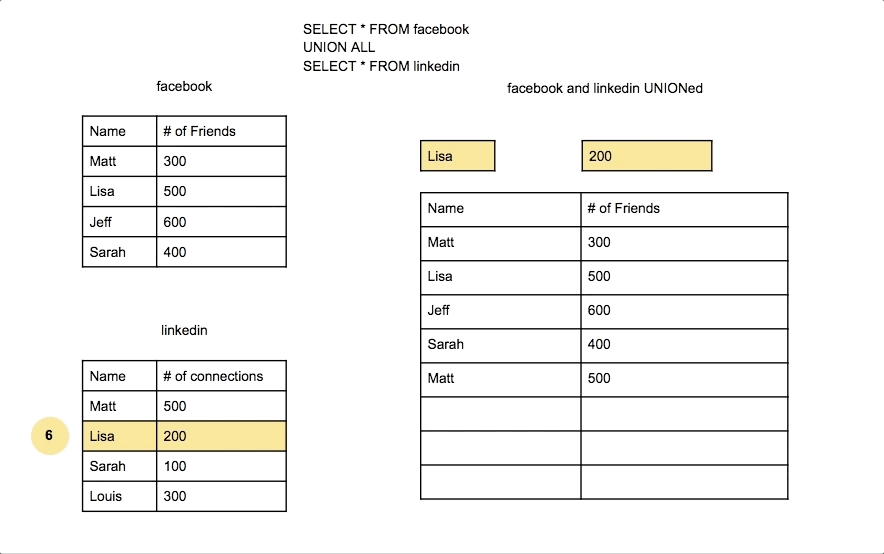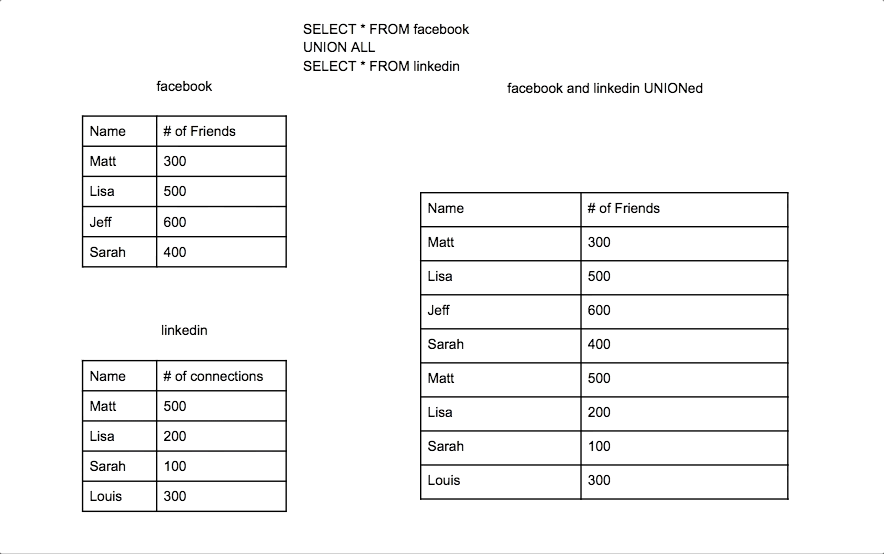
Union Join
A Union Join combines the results of two SELECT queries, removing duplicate rows by default. Each SELECT query must have the same number of columns, with similar data types.